
Electronic stethoscopes are advanced medical devices incorporating electronic components to amplify and enhance the sounds detected by the traditional acoustic stethoscope. They typically consist of a chest piece, similar to a traditional stethoscope, which contains a microphone to capture body sounds such as heartbeats, breath, and bowel sounds.
According to nlm, electronic stethoscopes address the issue of low sound levels by electronically amplifying body sounds. They achieve this by converting acoustic sound waves captured through the chest piece into electrical signals, which can then be amplified for enhanced listening clarity.
The captured sounds are then processed electronically, allowing for amplification, filtering, and sometimes even recording or transmitting capabilities. Electronic stethoscopes often feature adjustable volume levels, frequency filters, and noise reduction technology, enabling healthcare professionals to hear better and analyse body sounds even in noisy environments.
The Basic Functionality of Electronic Stethoscopes

Like traditional stethoscopes, electronic stethoscopes‘ basic functionality involves capturing body sounds using a microphone within the device’s chest piece. However, instead of directly transmitting these sounds through hollow tubing to the healthcare provider’s ears, electronic stethoscopes incorporate electronic components to process and enhance the captured sounds.
Here’s a breakdown of the basic functionality of electronic stethoscopes:
- Sound Capture: Like traditional stethoscopes, electronic stethoscopes feature a chest piece with a diaphragm or bell placed on the patient’s body to capture heartbeats, breath sounds, and bowel sounds.
- Electronic Processing: Once the microphone captures the sounds in the chest piece, they are converted into electrical signals. These signals are then processed electronically within the stethoscope.
- Amplification: Electronic stethoscopes amplify the electrical signals, making the body sound louder and easier to hear. The volume controls on the stethoscope can adjust this amplification.
- Filtering and Noise Reduction: Many electronic stethoscopes feature built-in filters and noise reduction technology to enhance the quality of the captured sounds. This helps to eliminate background noise and focus on the specific body sounds of interest.
- Output: The processed sounds are transmitted either through headphones worn by the healthcare provider or through built-in speakers on the stethoscope itself. Some electronic stethoscopes also offer the option to wirelessly transmit the audio to other devices such as smartphones or computers.
- Additional Features: Depending on the model, electronic stethoscopes may offer additional features such as recording capabilities, Bluetooth connectivity for data transfer, and visualising sound waveforms on a screen.
Benefits of electronic stethoscopes
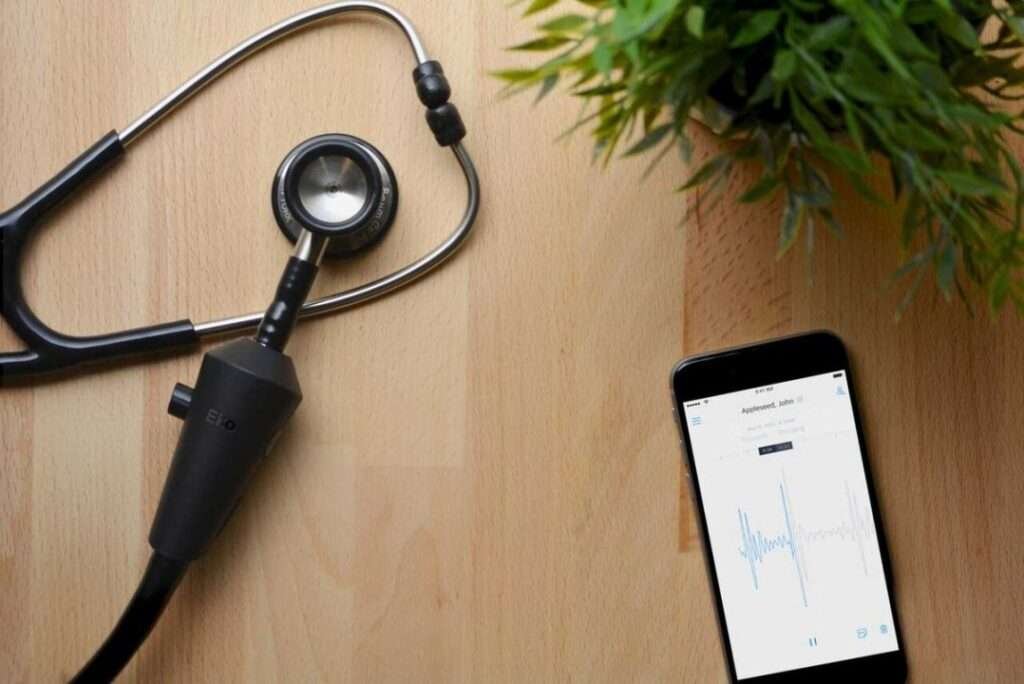
Electronic stethoscopes offer a range of benefits over traditional acoustic stethoscopes:
Improved Sound Clarity and Amplification: Electronic stethoscopes utilise advanced technology to amplify body sounds, making them louder and clearer. This enhanced clarity allows healthcare professionals to assess and diagnose patients more accurately.
Noise Cancellation
Electronic stethoscopes often incorporate noise cancellation technology, which helps to filter out ambient noise and focus on the specific sounds of interest, such as heart murmurs or lung sounds. This feature enhances the ability to detect subtle abnormalities and improves diagnostic accuracy.
Recording Capabilities
Many electronic stethoscopes come equipped with recording capabilities, allowing healthcare providers to capture and store audio recordings of patient examinations. These recordings can be useful for documentation, sharing with colleagues for consultation, or educational purposes.
Telehealth Applications
Electronic stethoscopes have great potential for telehealth applications, enabling remote patient monitoring and telemedicine consultations. Healthcare providers can use electronic stethoscopes to listen to patients’ heart and lung sounds in real-time during virtual appointments, facilitating diagnosis and treatment decisions even from a distance.
Customisable Settings
Electronic stethoscopes often feature customisable settings such as adjustable volume levels, frequency filters, and recording options. This flexibility allows healthcare professionals to tailor the device to their specific preferences and the needs of each patient encounter.
Types of electronic stethoscopes

There are primarily two types of electronic stethoscopes: digital and electronic.
Digital Stethoscopes (Connect to Apps)
Connectivity: Digital stethoscopes are designed to connect to smartphones or other devices via Bluetooth or USB. They often have companion mobile applications that allow healthcare professionals to visualise, record, and analyse auscultatory sounds directly on their smartphones or tablets.
Features
These stethoscopes may offer features such as sound visualisation in waveform or spectrogram format, recording and playback functionalities, and annotating or sharing recordings with colleagues for consultation.
Telemedicine Integration
Digital stethoscopes are well-suited for telemedicine applications, enabling remote patient monitoring and virtual consultations. Healthcare providers can transmit auscultatory recordings in real-time to specialists or use them for remote diagnosis and follow-up care.
Electronic Stethoscopes (Standalone)
Standalone Operation: Electronic stethoscopes function independently without connecting to external devices or apps. They typically have built-in amplification, noise cancellation, and other electronic processing capabilities.
Recording Capabilities: Some standalone electronic stethoscopes offer recording capabilities, allowing healthcare professionals to capture and store auscultatory sounds directly on the device for later review or documentation.
Customisable Settings: Electronic stethoscopes may feature adjustable volume levels, frequency filters, and other customizable settings to tailor the device to individual preferences and patient needs.
Additional Features: Depending on the model, electronic stethoscopes may include additional features such as heart rate monitoring, built-in educational resources, and compatibility with electronic health record (EHR) systems.
Considerations When Choosing an Electronic Stethoscope

When choosing an electronic stethoscope, several factors should be considered to ensure it meets the needs of healthcare professionals. Here are some key considerations:
Cost
Evaluate the cost of the electronic stethoscope and consider your budget constraints. Electronic stethoscopes vary in price depending on their features and brand reputation. While some advanced models may be more expensive, they often have additional functionalities to enhance diagnostic capabilities.
Features
Amplification Level: Assess the stethoscope’s amplification level to ensure sufficient sound clarity and volume for auscultation. Look for adjustable volume controls to tailor the amplification level based on individual preferences and patient needs.
Noise Reduction
Consider the effectiveness of the stethoscope’s noise reduction technology in filtering out ambient noise and enhancing the clarity of body sounds. High-quality noise reduction can improve diagnostic accuracy, especially in noisy environments.
Recording
Determine whether the stethoscope has recording capabilities and evaluate the recording quality. Recording functionalities can be valuable for documentation, sharing with colleagues, and reviewing patient assessments.
Connectivity
Decide whether you prefer a digital stethoscope that connects to mobile apps or a standalone device. Digital stethoscopes offer connectivity to smartphones or tablets, allowing for real-time visualisation, recording, and analysis of auscultatory sounds. Standalone electronic stethoscopes operate independently without requiring external devices or apps and may be preferred for simplicity and reliability.
User Comfort and Design
Comfort: Consider the stethoscope’s weight, size, and ergonomic design to ensure comfort during prolonged use. Look for features like soft ear tips and adjustable headsets for a comfortable fit.
Design: Assess the stethoscope’s overall design and construction quality. Opt for a durable, well-built device that can withstand daily use and potential drops or impacts.
Conclusion

In the dynamic realm of modern healthcare, the electronic stethoscope stands tall as a beacon of innovation, revolutionising how we listen to the symphony of the human body. With amplified clarity, noise reduction, recording capabilities, and connectivity options, these cutting-edge instruments empower healthcare professionals to diagnose with precision, collaborate seamlessly, and embrace the possibilities of telemedicine.
As technology evolves, the electronic stethoscope remains an indispensable ally in pursuing better patient outcomes and a testament to the enduring spirit of medical progress. Embrace the future of auscultation—where every heartbeat and breath tells a story of innovation and care.
